Hode
Authored by:: Brendan Langen
Hode (Higher Order Data Editor) is a Haskell program for reading, writing and searching what might be loosely termed a hypergraph. It’s like a knowledge graph, but more expressive – atoms and relationships can both be members of other relationships, which are labeled and can have any number of members.
Created by Jeffrey Benjamin Brown https://github.com/JeffreyBenjaminBrown
There are three branches to Hode: The RSLT data structure, the Hash language for describing subsets of an RSLT, and the UI, which lets you use the previous two things. A Rslt (Reflexive Set of Labeled Tuples) is a generalization of a knowledge graph. It lets a user easily represent any natural language expression. (A
Rsltis isomorphic to what some programmers call a “hypergraph” – but mathematicians claimed that term first, and in math it means something much less expressive.) ARsltis a collection of expressions, each of which is either a phrase (like “cats”), or a relationship (like “cats have noses”) or a template (like “_ have _”) shared by many relationships. What distinguishes aRsltfrom agraphis that relationships can involve any (positive) number of members, and a relationship can itself belong to other relationships. Hash is a language, close to ordinary natural language, for talking about expressions in aRslt. It offers a concise representation, both for individualExprs (expressions) in aRslt, and for queries to retrieve sets ofExprs. The UI displays expressions from your graph using the Hash language.
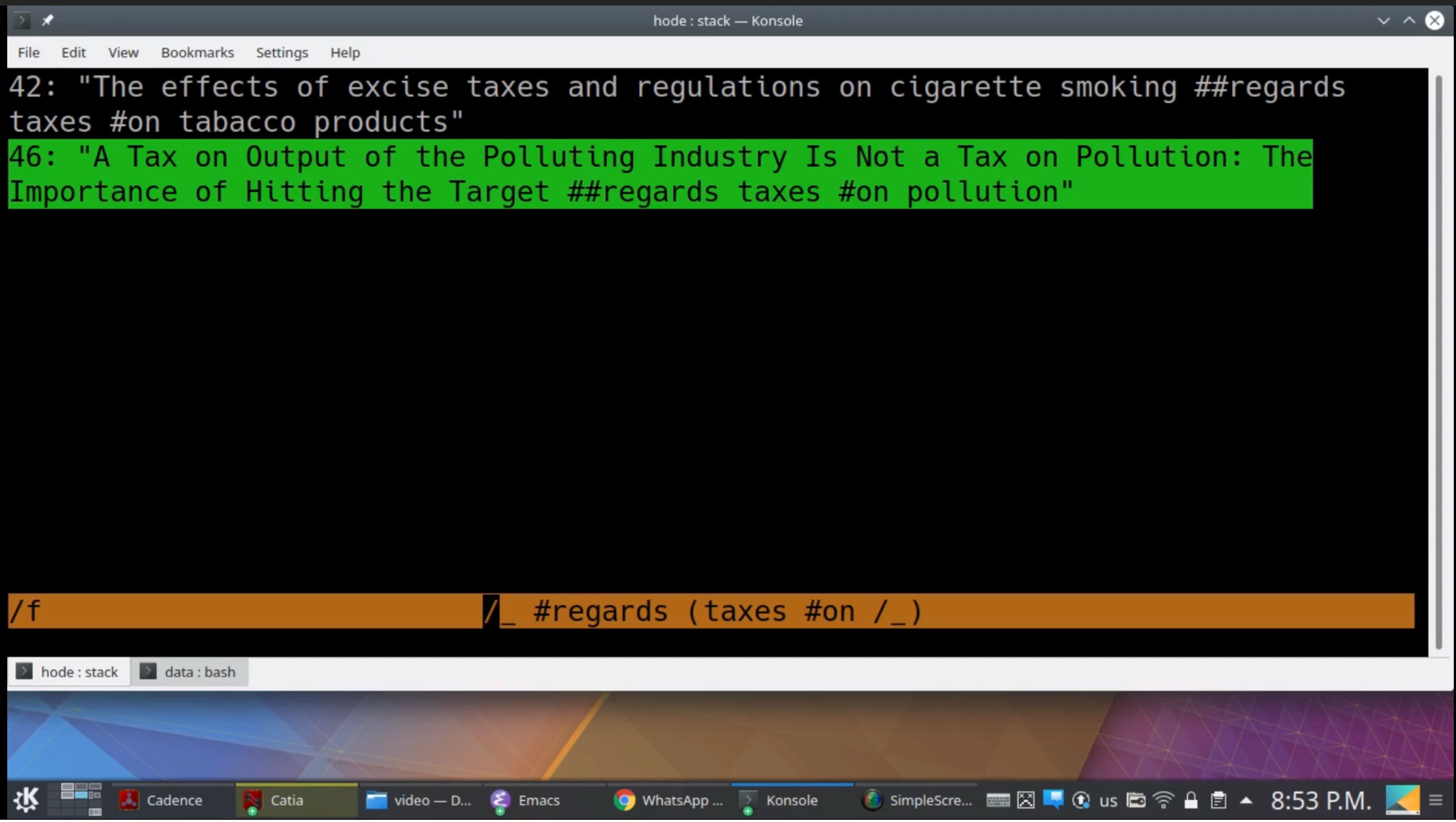
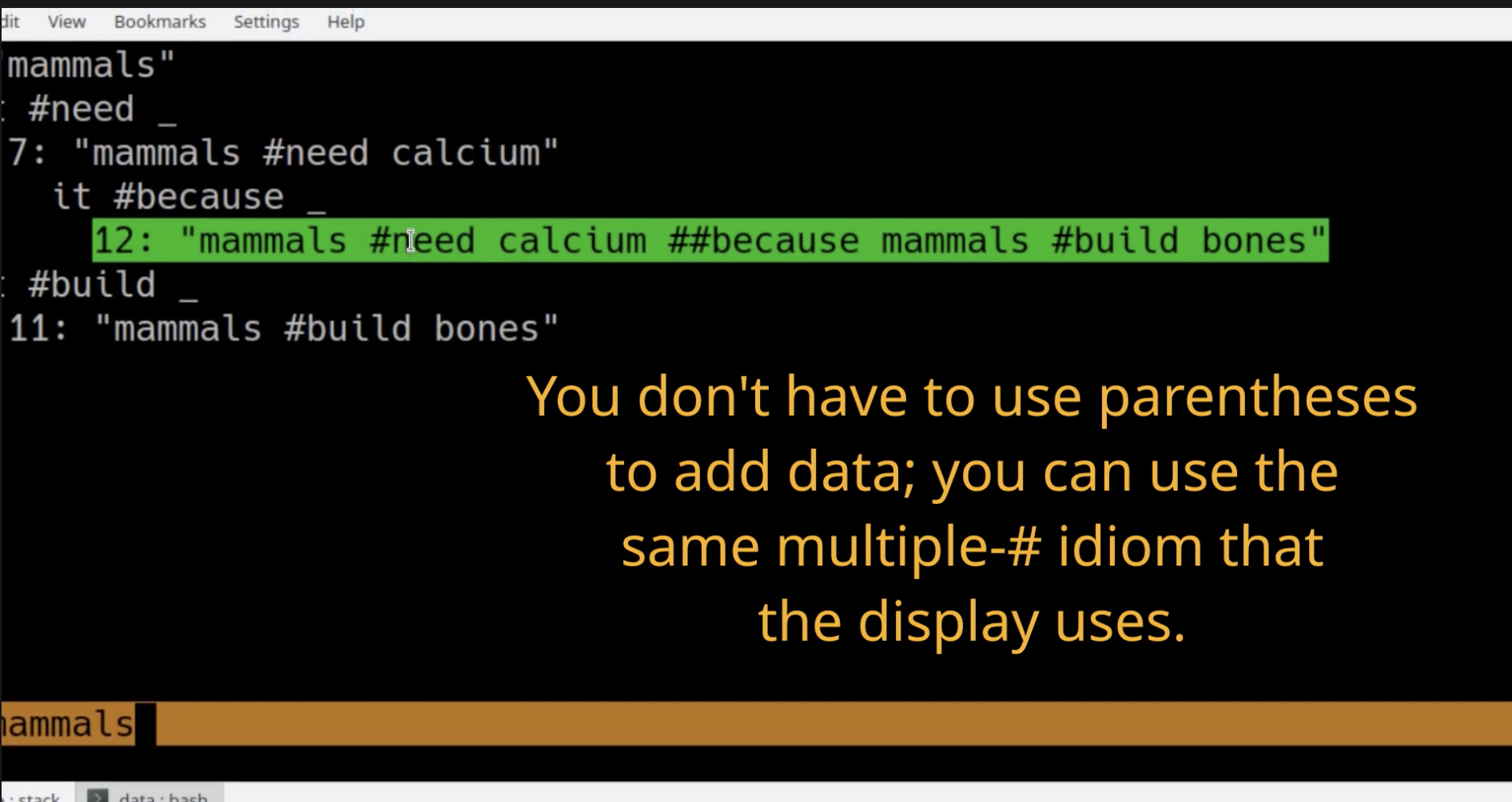
Examples in action.
| |
| |
| |
| |