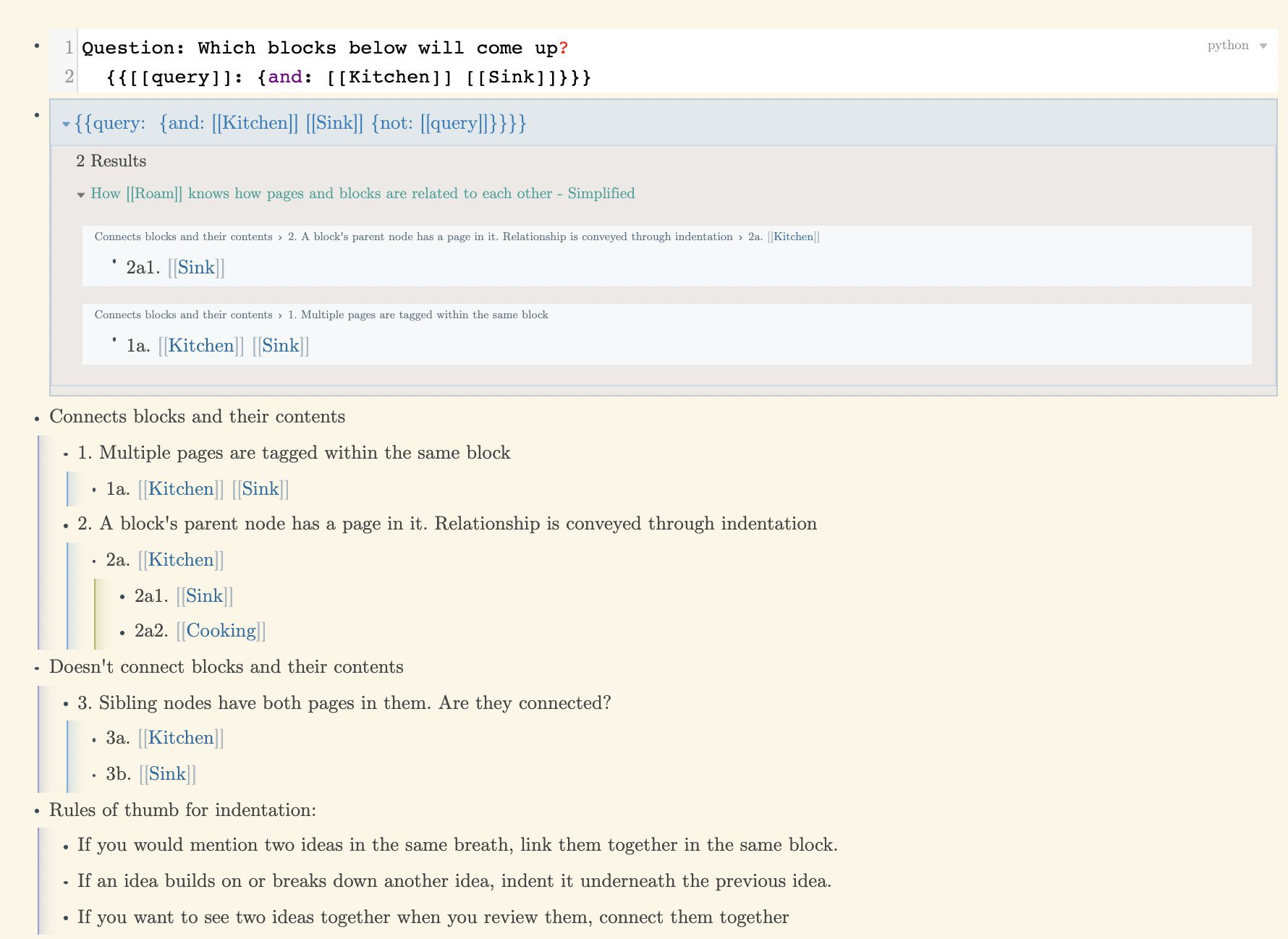
What are powerful primitives for a user of a decentralized knowledge graph?
Authored By:: Rob Haisfield
The design of a tool for thought’s primitives and its UX will influence the behavior of its users. For example, Roam designed its indentation and bidirectional link filtration to facilitate a Zettlekasten.
When I realized that the way that filtering/queries work with indentation can lead users to nest blocks in basically the same way as a folgezettel I was like “ @Conaw you dog.” Tangential to what @vgr is describing, but just shows how Roam excels at embedding philosophy in design twitter.com/vgr/status/134… Tweeted on Jan 4, 2021
Backlinks are displayed by as a collapsible list. The backlinks do not just display the titles of the pages where a backlink is present: they also show breadcrumbs of context from what came before the relevant block. see Search as a primitive
While you are looking through backlinks, you can filter them down by including and excluding items, which are sorted by their frequency.
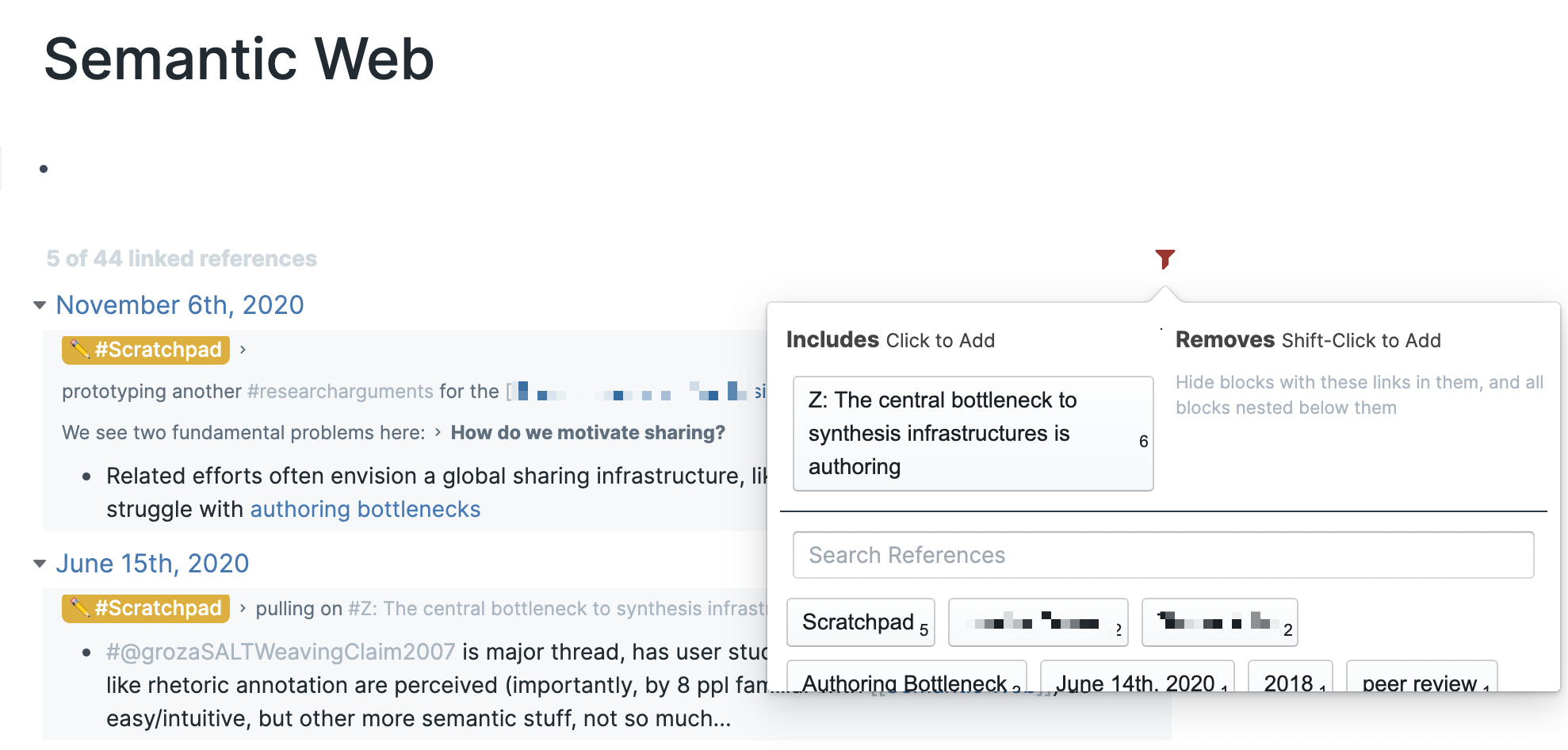
One could also argue that outliners push people towards divergence. In Roam, you can branch your thoughts, but it can be difficult to group them together. Sibling nodes are unrelated to each other, so it can be difficult to query for a block that contains a list of items nested beneath it. In its current form, it can only query one branch at a time.
Take a look at the backlinks for Roam Research and Obsidian. You can expand and collapse the list of results in each.
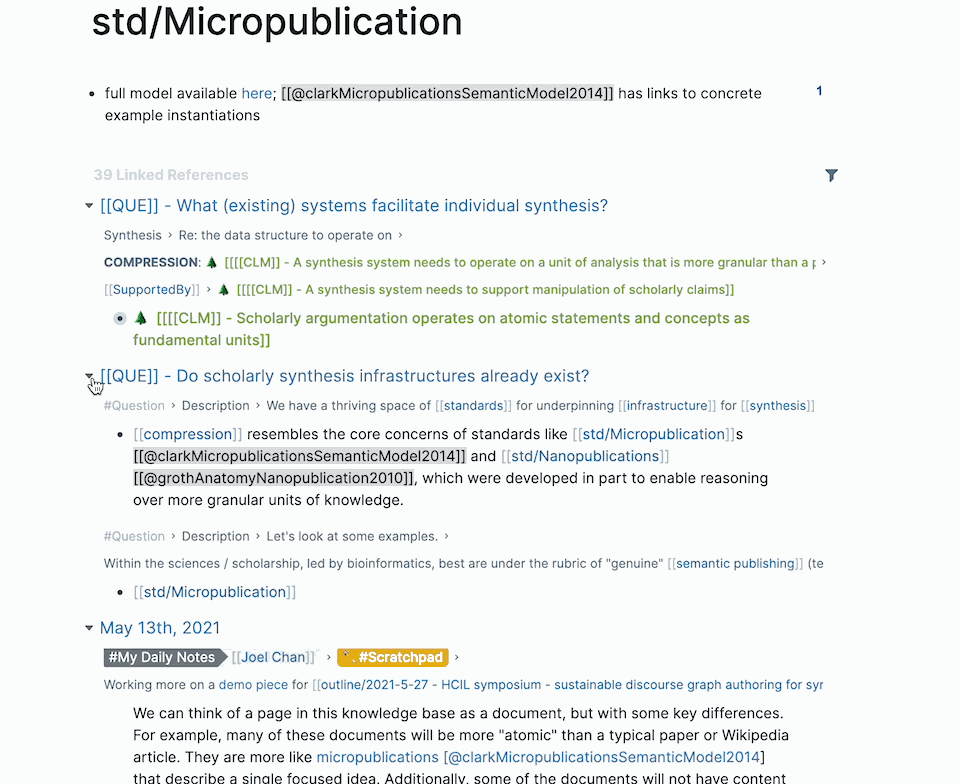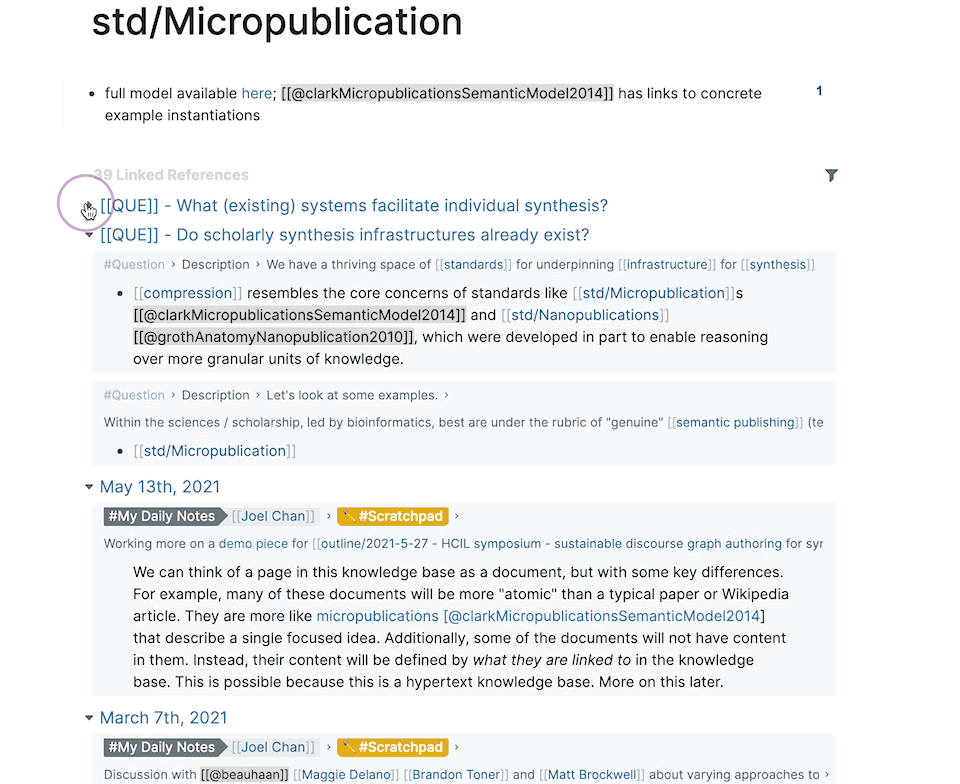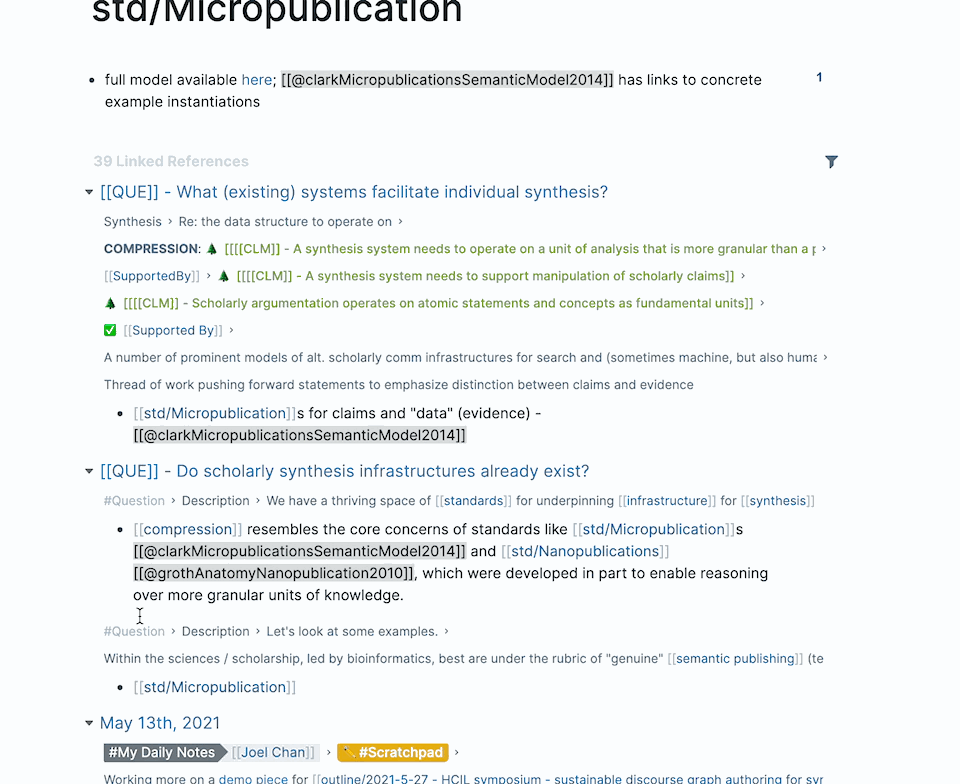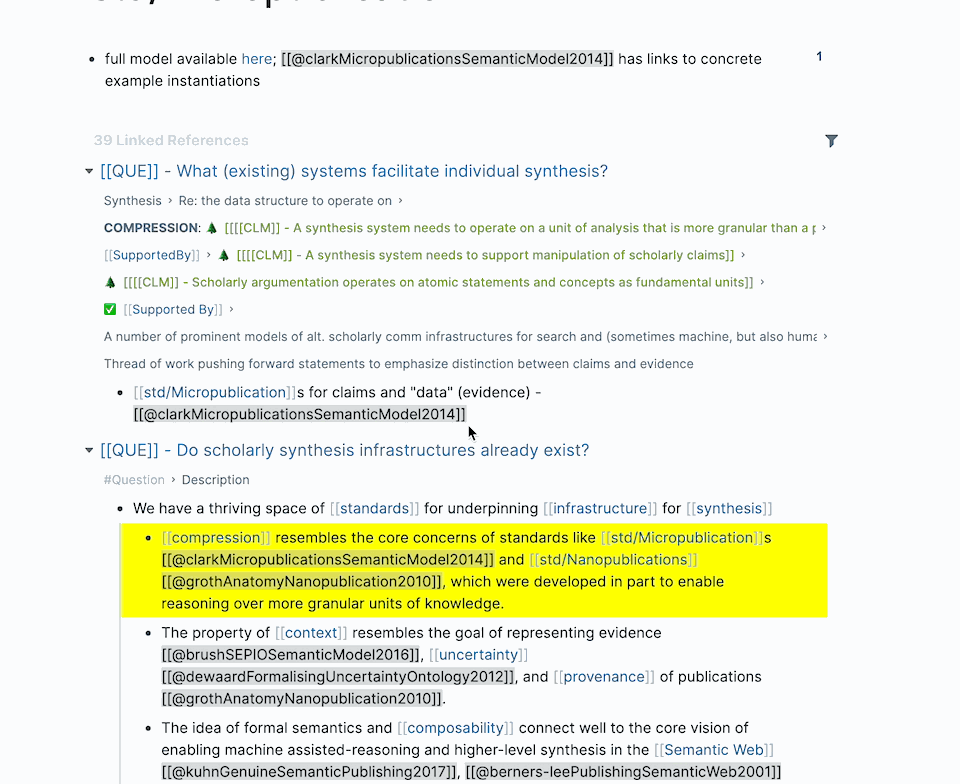
When there are too many results, you can filter to narrow the results
Users will have a primitive to write inline data structures
My current thinking is that the most valuable set of primitives are basically: typed concepts, typed relationships, expressive user-generated data structures, and rules. I want to be able to write in blocks with inline data structures, arbitrary relationships between blocks, block referencing, inline querying, and inline coding.
NLP, similar to Jump’s NLU, will enable users to implicitly instantiate complex mental models into the data structure. Expressive data structures (like triplets and nested tables) will enable people to manually specify structure when necessary. They should be expressive enough that many different visualizations can be made on top.